编写新的二维代价地图(Costmap2D)插件
![带有渐变演示的动画gif `[待校准@2043] <http://dev.nav2.fishros.com/calibpage/#/home?msgid=2043>`_](../../_images/gradient_layer_preview.gif)
概述
必要条件
假如ROS 2、Gazebo 和 TurtleBot3包是在安装或本地构建的。请确保 Nav 2项目也是在本地构建的,构建过程可以参考 编译和安装 。 [校准@小鱼]
教程步骤
1- 写一个新代价地图2D(Costmap2D)插件 [校准@小鱼]
为了方便演示,下面这个例子将创建代价地图(costmap)插件,然后放置重复代价梯度到costmap中。有注解代码可以找到本教程在 navigation2_tutorials 库的 nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin ROS 2d的包。当你自己想要创建2D代价地图插件时请参考它。 [校准@小鱼]
插件类 nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin::GradientLayer 继承于基类 nav2_costmap_2d::Layer: [校准@小鱼]
namespace nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin
{
class GradientLayer : public nav2_costmap_2d::Layer
基类提供了一系列虚函数 API处理costmap层插件。这些函数在运行 LayeredCostmap 时被调用 。函数列表,在插件的代码中的描述和是否必须实现情况见下表: [校准@小鱼]
Virtual method |
方法描述 |
必须重写? |
onInitialize() |
方法在插件初始化结束时调用。通常会在方法里声明ROS参数。任何需要初始化的操作都应该在该方法里完成。 [校准@小鱼] |
否 [校准@小鱼] |
updateBounds() |
方法问插件: 面积costmap层需要更新。有3输入参数方法: 机器人位置和定位4输出参数: 指针窗口边界。这些边界用于性能原因: 更新区域内窗口是新信息,避免更新整个costmap每次迭代。 [待校准@2056] |
是 [校准@小鱼] |
updateCosts() |
每次需要重新计算costmap时都会调用方法。它仅在其边界窗口内更新costmap层。方法有4个输入参数: 计算窗口边界和1个输出参数: 参考结果costmap |
是 [校准@小鱼] |
matchSize() |
方法在每次更改地图大小时调用。 [校准@小鱼] |
否 [校准@小鱼] |
onFootprintChanged() |
每次改变足迹(footprint)时都会调用方法。 [校准@小鱼] |
否 [校准@小鱼] |
reset() |
在costmap重置时可能有任何代码被执行。 [校准@小鱼] |
是 [校准@小鱼] |
在我们的示例中,这些方法具有以下功能: [校准@小鱼]
参数
GradientLayer::onInitialize()包含声明ROS参数的默认值: [校准@小鱼]
declareParameter("enabled", rclcpp::ParameterValue(true));
node_->get_parameter(name_ + "." + "enabled", enabled_);
并设置 need_recalculation_ 边界重新计算标志: [校准@小鱼]
need_recalculation_ = false;
GradientLayer::updateBounds()再次计算窗口边界,如果need_recalculation_值true并且无视need_recalculation_值而进行更新。 [校准@小鱼]GradientLayer::updateCosts()- 在这个方法中,是没有与前一图层合并,而是直接写入梯度到产生的成本地图master_grid。 这相当于内部工作costmap_并且调用updateWithTrueOverwrite()方法。以下是主成本图的梯度制作算法: [校准@小鱼]
int gradient_index;
for (int j = min_j; j < max_j; j++) {
// Reset gradient_index each time when reaching the end of re-calculated window
// by OY axis.
gradient_index = 0;
for (int i = min_i; i < max_i; i++) {
int index = master_grid.getIndex(i, j);
// setting the gradient cost
unsigned char cost = (LETHAL_OBSTACLE - gradient_index*GRADIENT_FACTOR)%255;
if (gradient_index <= GRADIENT_SIZE) {
gradient_index++;
} else {
gradient_index = 0;
}
master_array[index] = cost;
}
}
其中 GRADIENT_SIZE 是地图单元中每个梯度周期的大小, GRADIENT_FACTOR -每一步的成本图值的递减: [待校准@2070]
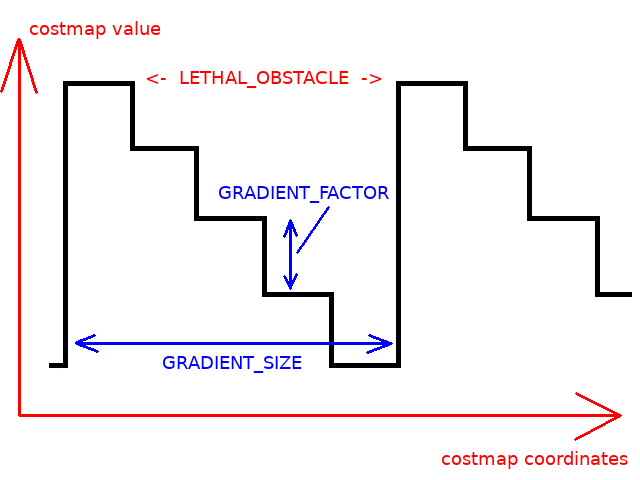
这些参数在插件的头文件中定义。 [待校准@2071]
GradientLayer::onFootprintChanged()just resetsneed_recalculation_value. [待校准@2072]参数``GradientLayer::reset()`` method is dummy: it is not used in this example plugin. It remaining there since pure virtual function
reset()in parentLayerclass必须被推翻。 [待校准@2073]
2-Export GradientLayer plugin [待校准@2074]
书面插件将加载运行时基本父类然后将调用插件处理模块 (costmap2d的 LayeredCostmap )。Pluginlib打开给定插件在运行时提供方法导出类调用。机制类导出告诉pluginlib基本类中使用这些调用。这允许扩展应用插件不知道应用源代码或重新编译它。 [待校准@2075]
在我们的示例中,“nav2_gradent_costmap_plugin:: gradentlayer” 插件的类应作为“ nav2_costmap_2d:: layer” 基础类动态加载。为此,插件应按如下方式注册: [待校准@2076]
插件的类应该用加载类的基本类型注册。为此,应该将一个特殊的宏
PLUGINLIB_EXPORT_CLASS添加到组成插件库的任何源文件中: [待校准@2077]
#include "pluginlib/class_list_macros.hpp"
PLUGINLIB_EXPORT_CLASS(nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin::GradientLayer, nav2_costmap_2d::Layer)
这部分通常放在写插件类的cpp文件的末尾 (在我们的例子中是 gradient_layer.cpp )。最好将这些行放在文件的末尾,但从技术上讲,您也可以放在顶部。 [待校准@2078]
插件的信息应该存储到插件描述文件中。这是通过在插件包中使用单独的XML (在我们的示例中是
gradient_plugins.xml) 来完成的。此文件包含以下信息: [待校准@2079]
参数``path``:路径和名称库插件放置。 [待校准@2080]
参数``name``: 关于插件类型可以参考
plugin_typesparameter (详见下一节)。它可以是你想要的任何东西。 [待校准@2081]参数``type``:插件类命名空间从源代码。 [待校准@2082]
参数``basic_class_type``:基本父类plugin类导出。 [待校准@2083]
参数``description``:插件描述文本形式。 [待校准@2084]
<library path="nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin_core">
<class name="nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin/GradientLayer" type="nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin::GradientLayer" base_class_type="nav2_costmap_2d::Layer">
<description>This is an example plugin which puts repeating costs gradients to costmap</description>
</class>
</library>
插件的导出是通过将 pluginlib_export_plugin_description_file() cmake函数包含到 CMakeLists.txt 中来执行的。此函数将插件描述文件安装到 share 目录中,并设置插件描述XML的属性索引,以便作为所选类型的插件发现: [待校准@2085]
pluginlib_export_plugin_description_file(nav2_costmap_2d gradient_layer.xml)
插件描述文件也应该添加到 package.xml 。 costmap_2d 是包的接口定义,我们机箱 Layer ,需要路径xml文件: [待校准@2086]
<export>
<costmap_2d plugin="${prefix}/gradient_layer.xml" />
...
</export>
一切完成后把插件封装成 src 目录一定ROS 2-workspace,构建插件包 ( colcon build --packages-select nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin --symlink-install ) 和源 setup.bash 文件有必要。 [待校准@2087]
现在插件可以使用了。 [待校准@2088]
3-在代价地图2D中启用插件 [待校准@2089]
下一步,需要告知代价地图2D有关新插件的信息。的插件应添加到 plugin_names 和 plugin_types 列表 nav2_params.yaml 可选用 local_costmap / global_costmap 为了启用在运行时间控制器/规划器服务器。 plugin_names 列表包含插件对象的名称。这些名字可以是你想要的任何东西。 plugin_types 包含列在 plugin_names 对象中的类型。这些类型应对应于插件描述XML文件中指定的插件类的 name 字段。 [待校准@2090]
备注
用Galactic或后, plugin_names 和 plugin_types 替换单个 plugins string载体插件名称。类型现在定义在 plugin_name 命名空间 ''plugin: `` field (e.g. `` 插件: MyPlugin: Plugin'')。内联注释代码块将帮助您通过这个。 [待校准@2091]
例如: [待校准@2092]
--- a/nav2_bringup/bringup/params/nav2_params.yaml
+++ b/nav2_bringup/bringup/params/nav2_params.yaml
@@ -124,8 +124,8 @@ local_costmap:
width: 3
height: 3
resolution: 0.05
- plugin_names: ["obstacle_layer", "voxel_layer", "inflation_layer"] # For Eloquent and earlier
- plugin_types: ["nav2_costmap_2d::ObstacleLayer", "nav2_costmap_2d::VoxelLayer", "nav2_costmap_2d::InflationLayer"] # For Eloquent and earlier
+ plugin_names: ["obstacle_layer", "voxel_layer", "gradient_layer"] # For Eloquent and earlier
+ plugin_types: ["nav2_costmap_2d::ObstacleLayer", "nav2_costmap_2d::VoxelLayer", "nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin/GradientLayer"] # For Eloquent and earlier
- plugins: ["obstacle_layer", "voxel_layer", "inflation_layer"] # For Foxy and later
+ plugins: ["obstacle_layer", "voxel_layer", "gradient_layer"] # For Foxy and later
robot_radius: 0.22
inflation_layer:
cost_scaling_factor: 3.0
@@ -171,8 +171,8 @@ global_costmap:
robot_base_frame: base_link
global_frame: map
use_sim_time: True
- plugin_names: ["static_layer", "obstacle_layer", "voxel_layer", "inflation_layer"] # For Eloquent and earlier
- plugin_types: ["nav2_costmap_2d::StaticLayer", "nav2_costmap_2d::ObstacleLayer", "nav2_costmap_2d::VoxelLayer", "nav2_costmap_2d::InflationLayer"] # For Eloquent and earlier
+ plugin_names: ["static_layer", "obstacle_layer", "voxel_layer", "gradient_layer"] # For Eloquent and earlier
+ plugin_types: ["nav2_costmap_2d::StaticLayer", "nav2_costmap_2d::ObstacleLayer", "nav2_costmap_2d::VoxelLayer", "nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin/GradientLayer"] # For Eloquent and earlier
- plugins: ["static_layer", "obstacle_layer", "voxel_layer", "inflation_layer"] # For Foxy and later
+ plugins: ["static_layer", "obstacle_layer", "voxel_layer", "gradient_layer"] # For Foxy and later
robot_radius: 0.22
resolution: 0.05
obstacle_layer:
YAML-file还可能包含每个插件的参数列表 (如果有),由插件对象名称标识。 [待校准@2093]
注意: 可能有许多同时加载的一种类型的插件对象。为此, plugin_names 列表应包含不同的插件名称,无论 plugin_types 是否保持相同类型。例如: [待校准@2094]
plugin_names: ["obstacle_layer", "gradient_layer_1", "gradient_layer_2"] # For Eloquent and earlier
plugin_types: ["nav2_costmap_2d::ObstacleLayer", "nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin/GradientLayer", "nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin/GradientLayer"] # For Eloquent and earlier
plugins: ["obstacle_layer", "gradient_layer_1", "gradient_layer_2"] # For Foxy and later
在这种情况下,每个插件对象将由其自己的YAML文件中的参数树处理,例如: [待校准@2095]
gradient_layer_1:
plugin: nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin/GradientLayer # For Foxy and later
enabled: True
...
gradient_layer_2:
plugin: nav2_gradient_costmap_plugin/GradientLayer # For Foxy and later
enabled: False
...
4-运行梯度层(GradientLayer )插件 [校准@小鱼]
运行Turtlebot3 仿真启用Nav2。如果你不知道如何仿真,请参考 入门 。下面是一些快捷命令: [校准@小鱼]
$ ros2 launch nav2_bringup tb3_simulation_launch.py
然后转到RViz,点击顶部的 "2D Pose Estimate" 按钮,指出地图上的位置,就像 入门 中描述的那样。机器人将被定位在地图上,结果应如下图所示。可以看到梯度成本图。还有两件值得注意的事情: 由 “梯度层::updateCosts()” 在其边界内的成本图和按梯度弯曲的全局路径动态更新: [待校准@2098]
![图像梯度costmap使用 `[待校准@2099] <http://dev.nav2.fishros.com/calibpage/#/home?msgid=2099>`_](../../_images/gradient_layer_run.png)